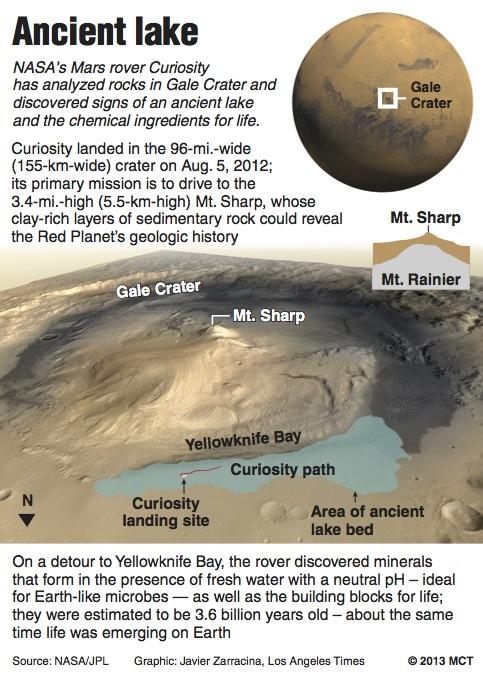
The Waters on Mars
When you think of Mars, what do you picture? Perhaps you imagine a dusty, red, rocky terrain upon which a couple of roving robots are wheeling around. Maybe you think of a cold, small planet that’s far away from the sun and devoid of life.
Possibly you only think of the new Matt Damon movie, The Martian. Whatever you picture, it probably does not include flowing water. However, evidence of such has just been found.
It has been theorized for decades that Mars used to have water on its surface, and presently, water frozen in its atmosphere and polar ice caps. It was not until recently that the idea of liquid water running on the planet seemed possible.
Why? For one, the average temperature on Mars is -67 0F (-55 0C), which, combined with a lower atmospheric pressure means that fresh water will either freeze or evaporate into the atmosphere, before it can even be used in liquid form.
Even in the warmer months, the highest point that the temperature reaches is 70 0F. At night, the temperature plummets to below freezing once again, meaning that the time frame H2O has to complete the change from ice to water is extremely short.
Miraculously, according to NASA, flowing water on the surface of Mars has been found. However, the water recently discovered is not fresh; rather it contains high concentrations of salts which allows the liquid to exist at sub-zero temperatures without freezing.
This means that in the warmer months, the salt water stays a liquid on the surface of the planet, and even goes so far as to flow through Mars’ mysterious terrain.
While this discovery may not seem like a big deal, it could be the answer to some major questions about the history of Mars. Did Mars once support life? If so, what happened?
While the water discovered is most likely too briny for life, (even microbial life) as we know it, to exist, the water on the surface opens up the possibility of fresh water being found under the surface of the planet. Water under the surface would be protected from the harsh elements and extreme temperatures, giving the potential for microbial life to exist and flourish.
This could give insight not only to the history of Mars, but also to the origin and history of our planet as well. Most importantly, the discovery of water could be a useful resource for when, hopefully in the near future, astronauts head to Mars to live and explore, giving us insight for the future of humanity in the universe.