Farthest Object in the Solar System?
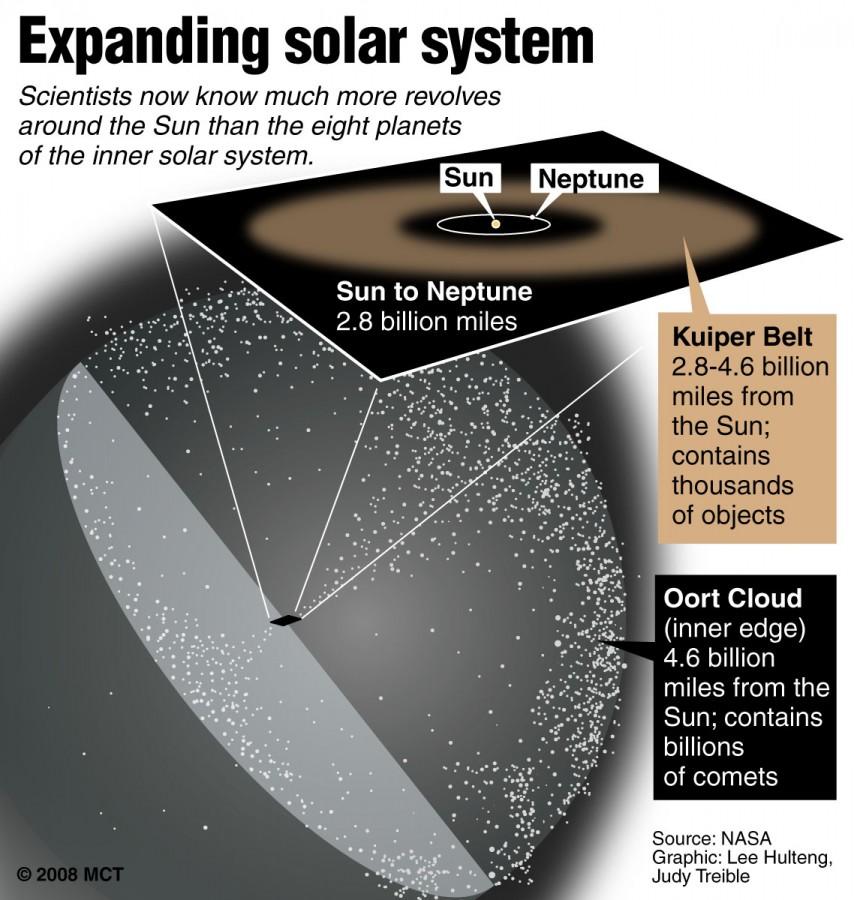
Drawing shows the relationship of the Kuiper Belt to the inner solar system and to the Oort Cloud. (McClatchy Washington Bureau by Robert S. Boyd)
Scientists have just discovered what may be the farthest known object in the solar system. The record is currently held by Eris, a dwarf planet that has been observed 14.6 billion km from the Sun. This new object, currently named V774104, is 15.4 billion km from the Sun, 103 times farther than Earth, and 3 times farther than Pluto!
V774104 is located beyond our known planets, beyond the ice-rich region around them called the Kuiper Belt, in the Oort Cloud. The Oort Cloud is a sphere-shaped region approximately 3 light years, or 30 trillion km, in diameter and marks the edges of the Solar System. Like most objects in the Oort Cloud, V774104 is extremely icy and is estimated to be 500 to 1000 km across, or about half the size of Pluto.
Scott Sheppard, an astronomer at the Carnegie Institution for Science in Washington, D.C., announced the discovery at the 47th annual meeting of the American Astronomical Society (AAS) Division for Planetary Sciences in National Harbor, Md., in November.
Sheppard & Chadwick Trujillo, an astronomer at the Gemini Observatory in Hilo, Hawaii, had discovered V774104 in October using Japan’s 8-meter optical-infrared Subaru Telescope on Mauna Kea.
Why is this discovery so important to astronomers?
Objects in the Oort Cloud are so far away from the Sun that their orbits are not influenced by the gravitational pull of the Sun or any of the Sun’s. This means that their orbits have remained mostly unchanged since the formation of the Solar System 4.5 billion years ago – a phenomenon scientists are eager to observe in order to learn more about the forces that influence our Solar System.
V774104 is the latest of many improvements astronomers have made to their range of observation; two other Oort Cloud objects have been identified in the past two decades. In 2003, a team led by Michael Brown, an astronomer at the California Institute of Technology, discovered the dwarf planet Sedna, which never approaches closer than 11.4 billion km to the Sun.
In 2012, Sheppard and Trujillo–the same team that discovered V774104–discovered 2012 VP113 (nicknamed “Biden”), an object that never approaches closer than 12 billion km to the Sun.
However, until scientists can confirm that V774104 does not approach closer to the Sun during its orbit, there is still a possibility that V774104 is simply a nearby object whose orbit has been stretched by Neptune’s gravity. Further observation is necessary before concluding whether or not V774104 has broken Eris’s record for farthest known object in the Solar System.
However, Sheppard told NPR, “This object is basically going to be interesting no matter what we find its orbit to be.”

Michelle Qin '19 is an editor for the Science and Technology section. As a senior, this is her fourth year of writing for The Banner. When she is not writing...